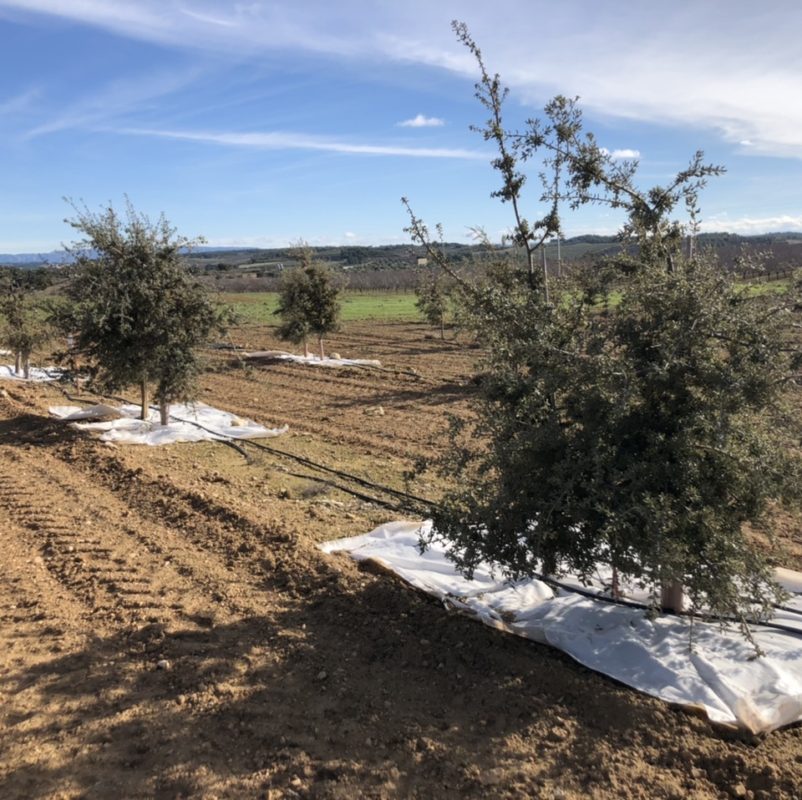
The results of a new study show that by means of a white mulching of the soil and with a small irrigation support, black truffle increases its competitiveness, thus adapting to Mediterranean climatic conditions. The article, published in the scientific journal Mycorrhiza, is signed by the Forest Sciences and Technology Centre of Catalonia and the University of Lleida.
According to these results, the application of techniques such as white mulching, which reduces warming and maintains soil moisture, and irrigation, which increases water availability, would allow modulating the harsh conditions resulting from climate change. In this way, mulching can be considered as an agricultural option for black truffle cultivation in Mediterranean areas where its habitat overlaps with the summer truffle, such as Spain, Italy and France.
The research evaluates the effects of irrigation application and three mulching treatments in an experimental truffle plantation with holm oak in Maials (Lleida), a municipality below the suitability ranges of the producing areas of the Pre-Pyrenees. The experiment combines black truffle and summer truffle, two of the most appreciated edible fungi worldwide, and describes their interaction. During 2 consecutive years, the team has monitored the evolution of the mycelium of the two truffles using molecular techniques.
The severity and frequency of drought periods can be detrimental to black truffle production
In recent decades, black truffle (Tuber melanosporum) plantations have been preferred by truffle producers, thanks to their high economic benefits and international demand. Even so, it can have difficulty adapting to changing climatic conditions, unlike the summer truffle (Tuber aestivum), which, although less interesting for cooking, does not depend so much on summer rainfall.
In recent decades, the recurrence of drought periods in Catalonia seems to be favouring the black truffle to the detriment of the summer truffle in the wild, as producers are observing. Therefore, “monitoring the dynamics of both truffle species under controlled conditions is key to understanding the most important factors affecting their cultivation and promoting better agricultural practices,” explains Yasmin Piñuela, a researcher at CTFC and the UdL.
In addition, the study concludes that more long-term studies are needed to evaluate the effects of different mulching materials on truffle production, for example, using biodegradable materials. It also recommends further research to test whether other factors, such as soil-specific microbial species, may also contribute to host tree growth.
More information:
Piñuela, Y., Alday, JG, Oliach, D., Castaño, C., Bolaño, F., Colinas, C., Bonet, JA, 2021. White mulch and irrigation increase black truffle soil mycelium when competing with summer truffle in young truffle orchard . Mycorrhiza. doi: 10.1007 / s00572-020-01018-x.
Supported by:
The Department of Agriculture, Livestock, Fisheries and Food and the Diputació de Lleida through the operation INNOVATRUF (PECT The Forest, the first resource of the green economy – European Regional Development Fund of the European Union-PO FEDER of Catalonia 2014-2020) and the Area of Sustainability (Departments of Farms and Environment).
Last modified: 25 February 2021